
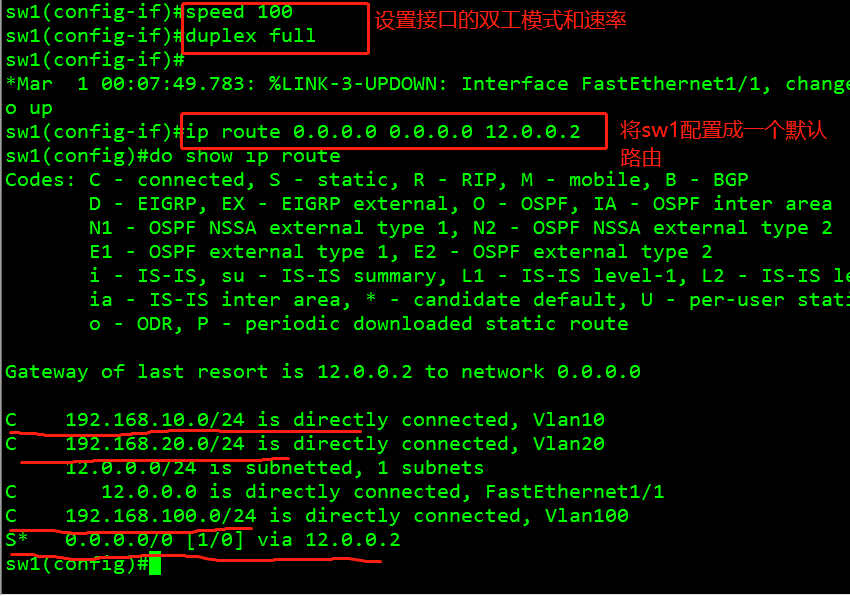

Centos 7 static ip speed duplex 100 mod#
To prevent the connection (here net-eth0) to restart after reboot, type: # nmcli con mod net-eth0 toconnect no Note: As before, you can specify the UUID (here 441085a4-4155-417b-ad8f-78a888d89988) instead of the network connection name.
To start a network connection (here net-eth0), type: # nmcli con up net-eth0Ĭonnection successfully activated (D-Bus active path: /org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/1) Note3: After reboot, the connection still restarts automatically, the property toconnect being set to yes, equivalent to ONBOOT=yes. Note2: You can specify the UUID (here 441085a4-4155-417b-ad8f-78a888d89988) instead of the network connection name. Note1: The - shows that the connection isn’t active any more (add the –active option to only display active connections). To stop a network connection from working (here net-eth0), type: # nmcli con down net-eth0 GENERAL.CON-PATH: /org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/0 GENERAL.CON-PATH: /org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/Settings/0 GENERAL.DBUS-PATH: /org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/0 To get all the information about a connection (here net-eth0), type: # nmcli con show net-eth0Ĭonnection.uuid: 441085a4-4155-417b-ad8f-78a888d89988 This command is deprecated and no longer displays the correct network configuration (secondary ip addresses, etc). Note2: Don’t use the ifconfig command any more.

Note1: ip a is a shortcut for ip address show, ip r a shortcut for ip route show. Below, you will see that the syntax when modifying a connection is different: it’s then using ipv4.addresses and a space between the ip address and the default gateway.ġ: lo: mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN Note4: ip4 and gw4 are used for respectively the ip address and the default gateway. Note3: nmcli con up net-eth0 is not necessary when initially configuring a connection. Note2: If you don’t specify the ip4 192.168.1.10/24 gw4 192.168.1.1 part, you end up with a connection automatically configured through DHCP. Note1: If you don’t specify con-name net-eth0, the connection is called ethernet-eth0. Note1: If a space appears in the interface name (like System eth0), put everything between quotes: nmcli con del “System eth0”. To remove a connection (here ethernet-eth0), type: # nmcli con del ethernet-eth0 Note: con is a shortcut for connection (you can even type only c).Īlternatively, you can type: # nmcli dev status To display the network configuration, type: # nmcli con showĮthernet-eth0 8d83684f-cd22-42cc-9fff-7704945a5c36 802-3-ethernet eth0


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
